How To Prove Parental Abuse, Neglect, Or Alienation In A Family Law Case
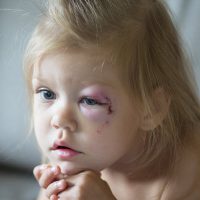
The Florida court’s default position is that it’s in the best interest of the child to have both parents in the child’s life. The courts will deviate from this position only when one parent brings allegations of parental abuse, neglect, or alienation. This would include situations involving domestic violence or allegations that one parent is unfit to raise the children. These are serious allegations that have serious penalties under Florida law. In this article, the Orlando divorce lawyers at Greater Orlando Family Law will discuss abuse, neglect, alienation and its treatment under Florida law.
Defining child neglect under Florida law
Florida Statutes 827.03 define child neglect as the failure of a parent to provide the child with the supervision necessary to maintain their mental and physical health. The courts will expect a parent to provide food, shelter, clothing, and medical services to the child as needed. The courts will also consider it neglectful to fail to protect the child from abuse or exploitation from another person.
Any parent who neglects their child can be found guilty of a third degree felony. Examples of neglect include:
- Unsafe living conditions, including health and safety code violations, squalid living conditions, and potentially hazardous conditions on the premises
- A lack of clothing or shelter for the children
- Failing to ensure the child has adequate nutrition
Proving neglect requires that you establish that the parent failed the child in one of the aforementioned ways. You’ll need to provide evidence that the child was neglected and the parent could have prevented the child’s neglect but did not.
Defining child abuse under Florida law
Florida statutes define child abuse as intentionally causing physical or mental injury to a child. Abuse is defined as any act that could reasonably be expected to cause bodily injury to a child. Child abuse is also considered a third degree felony under Florida law. Such allegations could impact a parent’s right to retain custody of their child. Examples of abuse include:
- Baby shaking
- Exploitation
- Malicious punishment that causes bodily harm
- Sexual abuse
Each parent has a duty of care to ensure that their child is not being abused by their spouse. In such cases, getting medical documentation of the abuse is paramount to proving that the child is in danger.
Defining parental alienation under Florida law
Parental alienation is when one parent manipulates the child to detest the other parent. Children who experience parental alienation may come to believe that the other parent is out to get them, hates them, or is unfit to raise them. They may provide imagined reasons why they don’t want to be around the other parent. In some cases, they will deny communication with the parent. Examples of parental alienation include:
- A spouse who refuses to comply with the custody agreement
- A child who refuses visitation with their parent
- When a child repeats negative communications that one spouse makes against the other parent
To prove parental alienation, a parent would need to establish that they hadn’t done anything negative to warrant the feelings that the child has towards them. The parent would need to establish that the other parent is manipulating the child to hate them. An experienced divorce lawyer can help in this matter.
Talk to an Orlando child custody attorney today
Greater Orlando Family Law represents the interests of parents who believe their child is being abused by their co-parent. Call our Orlando family lawyers today to schedule an appointment, and we can begin addressing your concerns right away.

